
- #HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD SKIN#
- #HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD FULL#
- #HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD PROFESSIONAL#
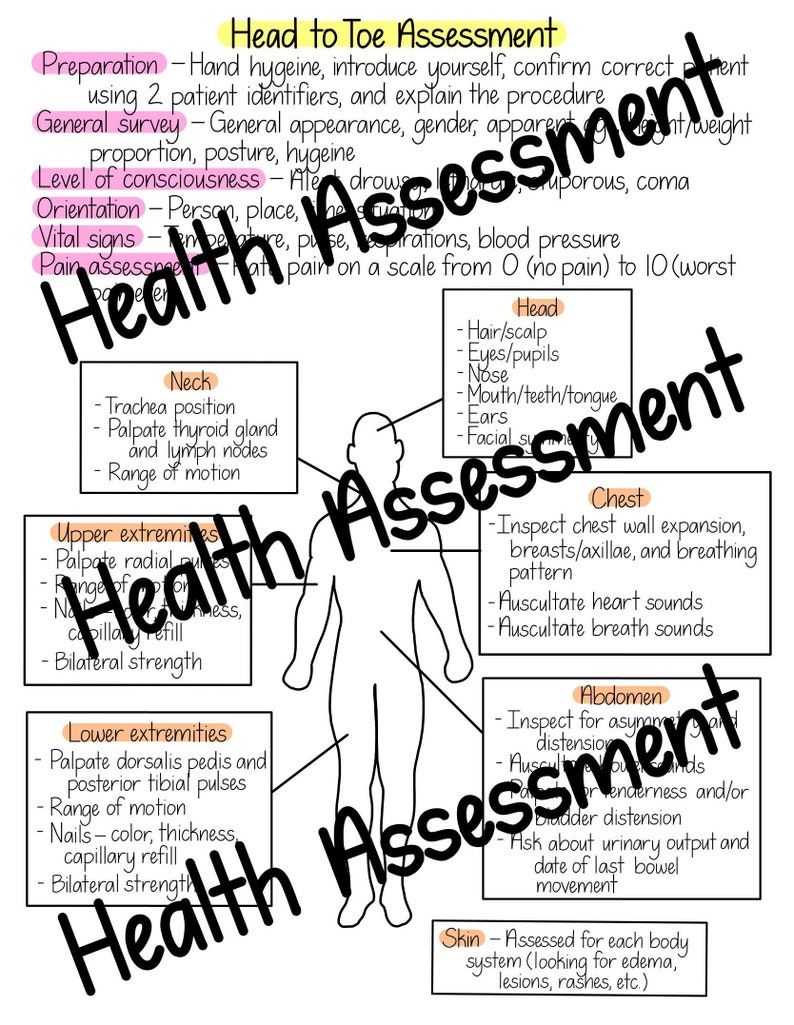
Pain and tenderness may indicate underlying inflammatory conditions such as peritonitis. Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds may be present after abdominal surgery, or with peritonitis or paralytic ileus. Hyperactive bowel sounds may indicate bowel obstruction, gastroenteritis, or subsiding paralytic ileum. Markedly visible peristalsis with abdominal distension may indicate intestinal obstruction. Determine frequency and type of bowel movements.Ībdominal distension may indicate ascites associated with conditions such as heart failure, cirrhosis, and pancreatitis.

Check urine output for frequency, colour, odour.Four quadrants for pain and bladder/bowel distension (light palpation only).

Note the heart rate and rhythm, identify S1 and S2, and follow up on any unusual findings with a focused cardiovascular assessment. Auscultate anterior chest blue dots indicate stethoscope placement for auscultation Auscultate posterior chest blue dots indicate stethoscope placement for auscultation Auscultate apical pulse at the fifth intercostal space and midclavicular line Unusual findings should be followed up with a focused respiratory assessment. The presence of crackles or wheezing must be further assessed, documented, and reported. Jugular distension of more than 3 cm above the sternal angle while the patient is at 45º may indicate cardiac failure. Use of accessory muscles may indicate acute airway obstruction or massive atelectasis. Apices and bases for any adventitious soundsĬhest expansion may be asymmetrical with conditions such as atelectasis, pneumonia, fractured ribs, or pneumothorax.For breath sounds anteriorly and posteriorly.Expansion/retraction of chest wall/work of breathing and/or accessory muscle use.Check pupillary reaction to lightĭry mucous membranes indicate decreased hydration.įacial asymmetry may indicate neurological impairment or injury. Unusual findings should be followed up with a focused neurological system assessment. Slow pupillary reaction to light or unequal reactions bilaterally may indicate neurological impairment. Drainage may indicate infection, allergy, or injury. Inspect mouth, tongue, and teeth for moisture, colour, dentures.Ĭheck eyes for drainage, pupil size, and reaction to light.Inspect eyes for pupillary reaction to light.Unilateral edema may indicate a local or peripheral cause, whereas bilateral-pitting edema usually indicates cardiac or kidney failure.Ĭheck hair for the presence of lice and/or nits (eggs), which are oval in shape and adhere to the hair shaft.
#HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD SKIN#
Redness of the skin at pressure areas such as heels, elbows, buttocks, and hips indicates the need to reassess patient’s need for position changes.
#HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD FULL#
Evaluating the skin, hair, and nails is an ongoing element of a full body assessment as you work through steps 3-9. Unusual findings should be followed up with a focused neurological system assessment.
#HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST COPD PROFESSIONAL#
The head-to-toe assessment includes all the body systems, and the findings will inform the health care professional on the patient’s overall condition. A comprehensive head-to-toe assessment is done on patient admission, at the beginning of each shift, and when it is determined to be necessary by the patient’s hemodynamic status and the context.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
